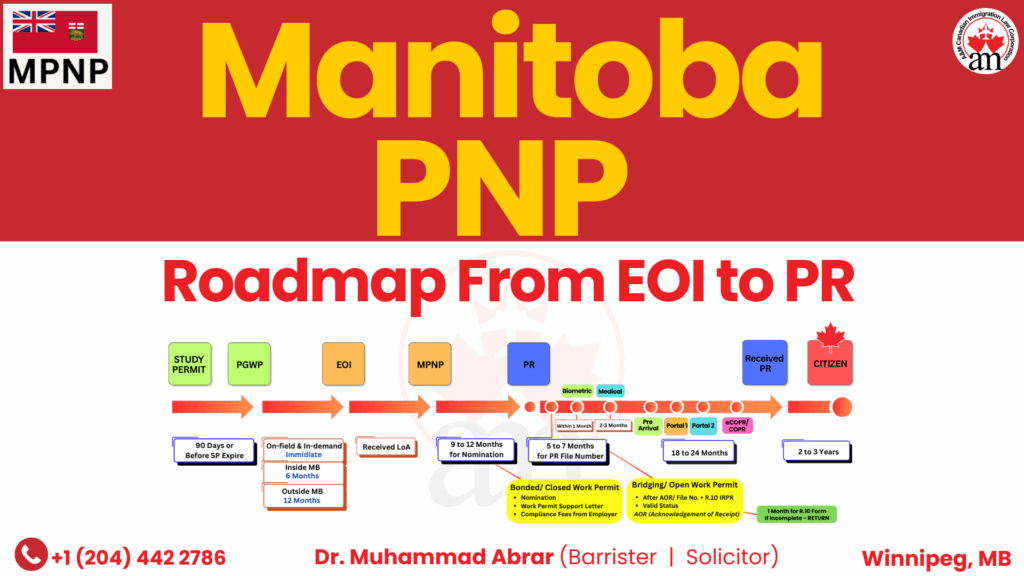
Upcoming Manitoba Public Policy 2026 Prediction
https://youtu.be/o4Y3eFMKt68?si=no6SVsIuAjdyMCpK This article is based on Manitoba’s past two years of Public Policies and predicts the upcoming changes expected in April 2026. Starting April 2026, the Manitoba Provincial Nominee Program (MPNP) is expected to accept applications for a Work Permit Support Letter. Who will be eligible? Only those whose work permits: Expired in 2025 or 2026, or Will expire within the next 45 days …will qualify to apply for a two-year Manitoba-specific work permit extension. Scenarios Covered (based on past policies) Applicants may qualify if they: Hold a valid work permit expiring in 2026 Held a valid work permit in May 2025 Have status expired but applied for a work permit or Visitor Record Are maintaining status Have status expired but applied for restoration In all scenarios, the candidate must have held a valid work permit on May 2025. Additional Requirements To be eligible, you must also: Have a valid MPNP Expression of Interest (EOI) profile in January 2026 Be residing in Manitoba prior to January 2026 Required Documents Letter of employment Copy of your current work permit Copy of your Expression of Interest profile Key Notes You can apply for a Work Permit Support Letter up to 45 days before your work permit expires. Visitor Record holders will also be eligible. If you already received a Letter of Advice to Apply (LOA), you will not be eligible. If your EOI expires, you must reapply to remain eligible. If approved, you will receive a two-year open work permit. If your NOC is eligible for family sponsorship, your spouse or children may also qualify for work permits. Final Advice Submit your EOI before 2026 Keep your status valid or maintained during 2026 Follow the rules to extend your work permit through public policy Stay tuned for more immigration updates and predictions. Book your first free in-person appointment today with an immigration lawyer.